All Articles
神奇的Node.js map中+=async问题
1. 看代码
东西都不复杂,看代码就完事了,一共是4个代码片段
map 中进行 += await
const f = (x) => Promise.resolve(x);
(async () => {
let total = 0;
await Promise.all(
[1, 1, 1].map(async (x, i) => {
console.log('exec', i);
console.log('b', total);
total += await f(x);
console.log('a', total);
})
);
console.log('done', total);
})();结果如图:
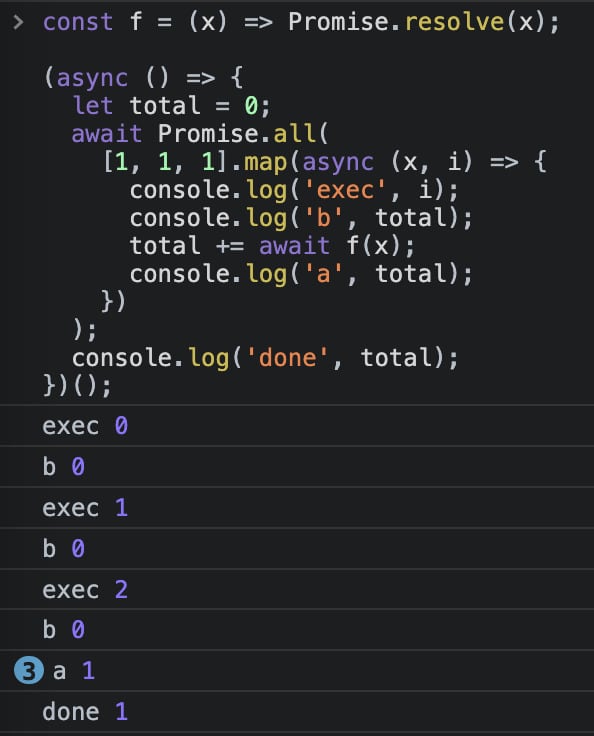
map 中进行 =赋值 然后+=
const f = (x) => Promise.resolve(x);
(async () => {
let total = 0;
await Promise.all(
[1, 1, 1].map(async (x, i) => {
console.log('exec', i);
console.log('b', total);
const r = await f(x);
total += r;
console.log('a', total);
})
);
console.log('done', total);
})();结果如图:
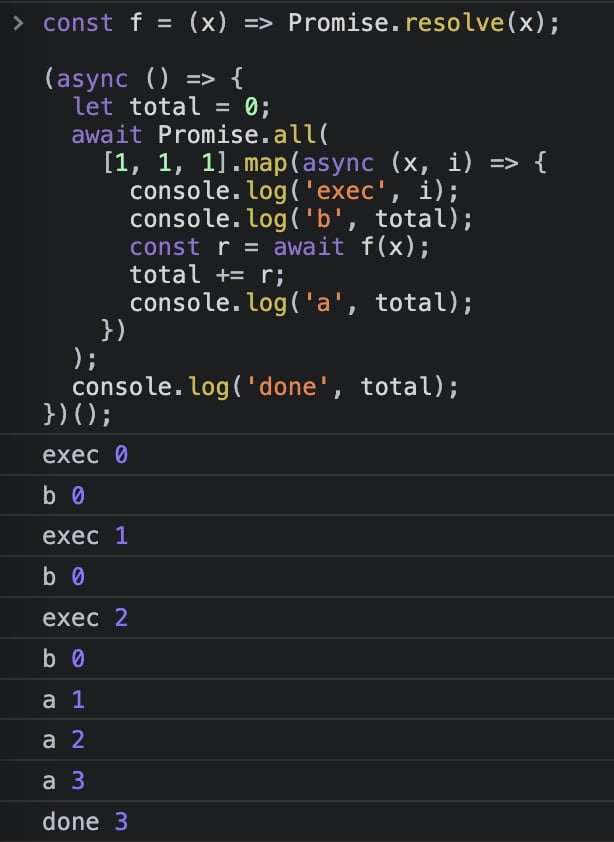
map 中进行 = await +
const f = (x) => Promise.resolve(x);
(async () => {
let total = 0;
await Promise.all(
[1, 1, 1].map(async (x, i) => {
console.log('exec', i);
console.log('b', total);
total = await f(x) + total;
console.log('a', total);
})
);
console.log('done', total);
})();这个结果和图2相同,也就是和上面一组相同
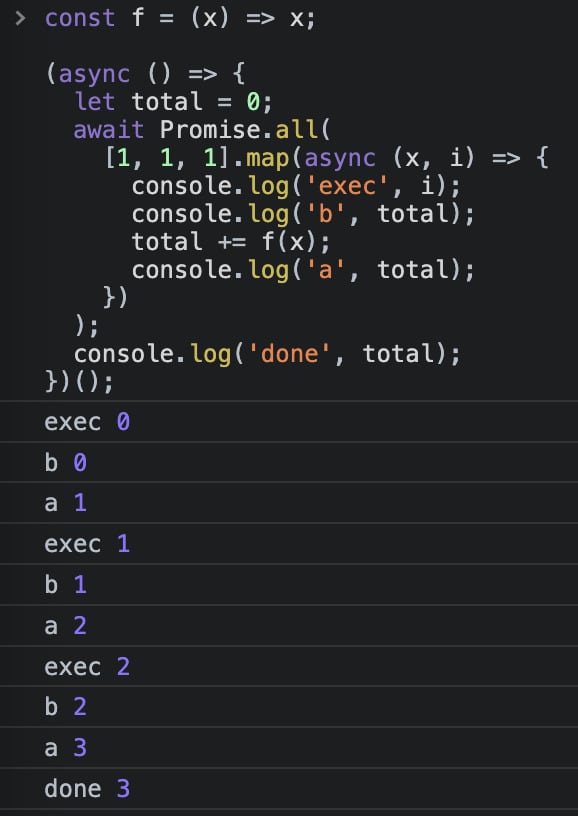
map 中进行同步 +=
const f = (x) => x;
(async () => {
let total = 0;
await Promise.all(
[1, 1, 1].map(async (x, i) => {
console.log('exec', i);
console.log('b', total);
total += f(x);
console.log('a', total);
})
);
console.log('done', total);
})();结果如图:
2. 原理
原理一点都不复杂,稍微想一下就知道了。这里主要是要注意这种case的发生,需要有意识地规避。因为结果比较反直觉,就算是有经验的程序员也会犯错。
EOF